How are climate change, the construction industry and BIM connected?
It is common knowledge now that the construction industry is one of the major culprits of the ecological footprint. The cement industry alone is in third place for the production of CO2 after the countries of China and the USA. Time is running out, and all designers in the sector need to begin to work collaboratively to the transition towards more sustainable paths.
However, designing zero energy buildings is not enough. We must also reduce the use of materials that pollute excessively and the overly exploitation of natural resources. We need to put in place plans for reusing and recycling, and the materials to recycle should come also from waste, and not only from the demolition of buildings.

In Copenhagen, during the conference organized on December 7th by KEA (Copenhagen School of Design & Technology), it was underlined the importance of architects and engineers considering the use of appropriate materials already in the preliminary design phase. Also important is limiting the use of reinforced concrete to those buildings and structures that really need it and, wherever possible, considering alternative solutions that can be even more performing. It is also necessary to reuse the material resulting from demolitions in a smart way.
In France and Denmark, in application of the European recommendations for the reduction of the ecological footprint, the law requires the declaration of the total of CO2 produced. Not only as LCA, i.e. a simple certification of how much CO2 that particular building produces, but it is also required to justify the choice on the materials, which must produce less CO2 than alternative solutions.
During the debate following the conference it was rightly pointed out that "virgin" materials often have a lower cost than the recycled ones because the production process from raw materials is simpler than the recycling of existing materials, especially if their composition is unknown. Soon however, to encourage recycling, in Denmark it will be introduced a tax on the production of CO2, which will make the price of the two choices comparable and will possibly make recycled materials more advantageous.
In Denmark, they initiated pilot cases in which, for example, it was approved the project of a nursery school in place of an old abandoned school, provided that the materials derive from the demolition of the old structure. In place of the old school there are now two soccer fields and a nursery school built sustainably and on a zero impact criteria. This thanks to the saving of "virgin" material which normally requires a large energy contribution, both in production and for transportation. Furthermore, wood has once again become the first choice, both for new houses and for renovations.
The role and contribution of BIM in all of this was also discussed. A software was shown that BIM allows to evaluate the CO2 footprint, just as there are already 4D and 5D software that allow to evaluate times and costs. Each product is connected with its ecological footprint, i.e. with the carbon dioxide produced for its production. In this way, it is possible for the designer to attribute a real value to the ecological footprint of the entire building.
It is clear that the role of material producers is becoming more and more Impactful. They must transition from providing the values that certify the "ecological footprint" in simple pdfs, to the transmission of data that can be directly read by design software. To allow this, the bSDD is already available, i.e. a service that buildingSMART International makes available to "translate" any property and geometry into data that can be read by modeling software.
Essentially, it is enough to connect these properties and values to each element. As an example, the "wall" properties can be linked to reinforced concrete, solid bricks, hollow bricks, laminated wood, recycled panels and so on to which the manufacturer will have to associate the corresponding "CO2/metre" properties. The software, at that point, can directly calculate the final footprint.

By changing the material, in a few clicks, the final value can automatically be updated. This will facilitate the final selection.
However, there is still a long way to go. For example, we need to work on new legislative instruments that support this approach. In public tenders, it will be necessary that the ecological footprint has a weight in the selection, so that designers are encouraged to make more ecological choices. It will also be important to help small producers of recycled materials to certify their products with the CE mark in order to be able to place them in the market. It will also be necessary to properly train manufacturers and the workforce to use these new products correctly. Finally, it will be necessary to support research in this sector.

These topics will also be addressed during the next buildingSMART International Summit, which will be held in Rome from 27 to 30 March 2023.
All the European chapters of buildingSMART will also meet, on this occasion, with the European Commission (DG Growth) to look for agreements to ensure that part of the substantial funding foreseen for the construction sector will be directed to these activities. We invite you to participate numerous at the Summit, that is open to all interested parties in the sector, members and non-members of buildingSMART.
Presentation and images by Lene Espersen
Article by Anna Moreno and Caterina Nissim
Digitalisation: what is changing for architects?
An interview with Veronika Schröpfer, Head of EU Research Projects at the Architects’ Council of Europe
>> Digitalisation is changing the work of architects around the globe. At the moment there are around 560.000 architect in Europe, most of these working alone or in small offices. SMEs have the advantage to be quicker to adapt to new technologies and tools. Architects have shown themselves to be extremely willing to learn, more than half of those using each tool are self-taught. Architects are much more likely to use new tools out of personal or business interest than due to client or regulatory requirements. This shows that architects are enthusiastic to adopt digitalisation tools.
The role of the development of digital competences in the building domain
>> Architects contribute around 17 billion Euros to the EU economy (ACE, sector study 2020). Nevertheless, ACE has advocated for more diversity in software and tool providers. Annual licence fees for software can be a barrier for micro sized architecture practices. They cannot afford various licences for similar tools but different providers depending on the project. Hence the interoperability of tools and platforms are vital.
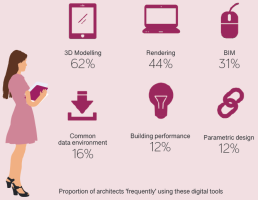
>> You can see in our 2020 ACE sector study, that there has been a proliferation of new digital tools which the architectural profession is adopting. A majority of architects use 3D modelling tools ‘frequently’, and nearly half use rendering tools frequently. About one in three architects frequently use BIM on their projects. An important aspect is that most architects use the tools out of their own choice.
The impact of putting in place a recognition system valid at European level
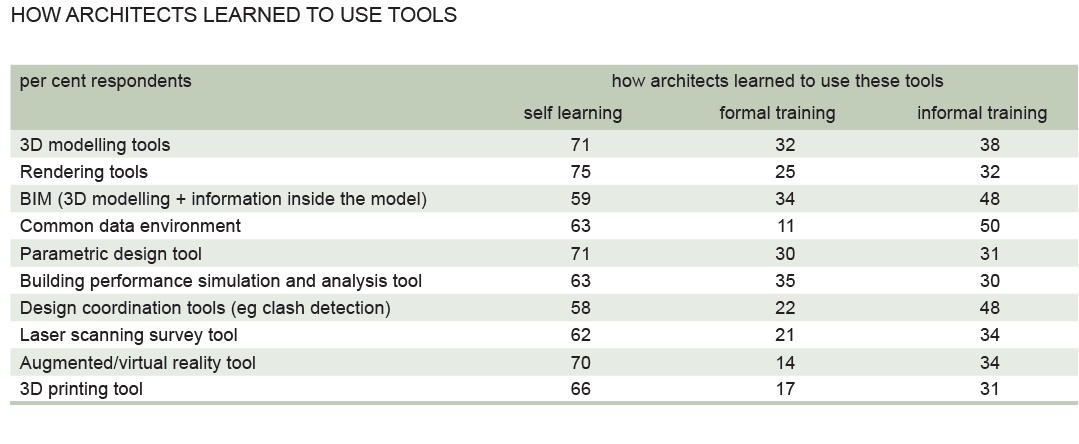
>> Our 2020 ACE Sector Study has revealed that the vast majority of architects taught themselves how to use digital tools.
No more than 35 per cent received formal training for any of the tools, although more received informal training. On average architects spend about 20 hours of official Continuing Professional Development (CPD) per year. CPD is a structured way of maintaining and developing the competence as a qualified professional by engaging in regular learning activities. For a training recognised and valid at EU level it should be endorsed by ACE Member Organisations in various EU Member States and meet the minimum agreed European quality standards. Various European training bodies should recognise each other’s CPD, making it easier for architects to work in the countries they choose. Usually, one learning hour equals one international CPD credit. Therefore, we joined the ARISE project, as it will work on the recognition of the CPD competences through the development of a platform based on microunits certified with blockchain.
Dr. Veronika Schröpfer, Head of EU Research Projects at the Architects’ Council of Europe
Images and sources of numbers from the ACE Sector Study: https://www.ace-cae.eu/fileadmin/user_upload/2020ACESECTORSTUDY.pdf
Revolutionising the learning process by changing the face of delivery and recognition of sustainable energy skills in the construction sector
That’s the target for the ARISE project team as they seek to deliver their new EU wide skills and training project, boosting thereby market uptake of qualified workforce.
ARISE has secured a €1.12M grant from the Horizon 2020 Work Program: Building a Low-Carbon, Climate Resilient Future: Secure, Clean and Efficient Energy, under the Call: Increasing Market Demand for Sustainable Energy Skills in the Building Sector.
ARISE’s mission is to support the twin transition of the construction sector and to contribute thereby to the European Recovery and Resilience Plans 2021-2027, by providing the construction sector workforce with digital and sustainable energy skills of the future, along with demand-side guidelines for marketable appreciation of skills and exploitation of benefits thereof.
Through a highly innovative approach, ARISE will deploy a system coupling methodology and approach, and encompassing:
1) Skills delivery method;
2) Learning accounts transaction and recognition;
3) Matrix of skills maturity, leading to new qualifications and jobs;
4) Profession–based learning content;
5) Impacts of skills on buildings’ energy performance;
6) New market and regulatory models of skills demand; and
7) Stimulation of investments in high energy performance buildings.
Engaged in the project demonstration stage, over 1000 stakeholders across Europe will improve their skills and competences, providing therefore project induced impact of over 4.5 million kWh/year of energy savings, 2.25 million kWh/ year of RES energy generation, reduction of GHG emissions by over 3.5 tons/year and initiation of 1.3 million EUR/year of investments in NZEBs. As a long–term cumulative impact, ARISE aims to contribute by over 75 million kWh of clean energy use in buildings and over 8,7 million EUR of green investments.
ARISE will revolutionise the learning process by monetising skills development and learning exchange with a digital system based on skills recognition rather than accreditation. The training and transaction system developed by the project will reward learners as they achieve competence at a certain level with the crypto currency for skills exchange: CERTcoin, the innovative currency of skills and learning of the construction sector embracing today’s digital transformation benefits. The learners’ CERTcoins, based on skills and time credits will be stored in an Individual Learning Account and can be used as digital points accumulation for example in a skills barometer or for exchanging it into valid certificates. It will be an easier accessible, less time consuming and still competitive way to upskill blue and white collars, as well as market-demand side, public administration, clients and owners
ARISE will apply digitalisation both as a learning method and as a framework of job-based construction skills of the future, multiplying the effects of the green transition skills. The novel training method will make the learning process attractive and effective, facilitating its accessibility through a mobile (smartphone) and a user–friendly, web-based platform. The intervention / learning progress will be achieved in a scalable way, in bite-sized skills delivery. ARISE will apply digitalisation and the earning of learning credits in a "step by step" recognition of competences, as an accelerator to empower demand for sustainable energy skills in the construction sector, and as an enabler of formal certification. This system will be employed based on blockchain procedures to instil transparency and trust.
ARISE utilises a circular economy approach specifically utilising digital skills stimulation and delivery across the entire building life cycle and assets to decarbonise the complete energy cycle. This approach harnesses the market drivers from the demand side and matches these with impact targeted strategies and objectives required to achieve comprehensive success. ARISE represents a multi faceted approach to tackle the carbon footprint of the construction sector. It is a pioneering training scheme AND a powerful socio - economic cross sectional influencer, affecting the multiple sectors of education, industry, market, and policy by delivering a dynamic training and market uptake model
The project led by Belfast Metropolitan College with eight other European partners will be launched in September 2021. Within 28 months, until December 2023, partners will work on development and demonstration of the innovative on demand training scheme for digitalisation towards sustainable energy skills, aimed at both supply and demand side.
The nine partners in the project consortium are:
- Belfast Metropolitan College, Northern Ireland
- Technological University Dublin, Ireland
- Institute for Research in Environment, Civil Engineering and Energy, North Macedonia
- ISSO, The Netherlands
- Conseil des Architectes D Europe Brussels
- IBIMI Institute for BIM- Italy
- Building Changes, B.V. The Netherlands
- Copenhagen School of Design and Technology Denmark
- Instituto Superior Technico, Portugal